All you need to know about Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW)
To make sound business judgments, it is necessary to take a comprehensive strategy supported by actual data. However, this is frequently not practicable since organizational departments typically function in silos.
 5 minute
5 minute


It is impossible to stress the necessity of maintaining a cohesive information system for making informed judgments. That is why companies utilize corporate data warehouses to concentrate their data.
We've seen the consumerization of ideas like predictive analytics, artificial intelligence, and conversational interfaces — all powered by data — during the last four years. However, despite the hoopla, most firms continue to struggle to exploit data in a meaningful way.
This blog post will help you understand the enterprise data warehouse, its concepts, how businesses can leverage it, and most importantly how we can deploy it to modernize your business. Let’s begin:
Table of contents
1. Introduction
2. What is enterprise data warehouse (EDW)?
3. Components of enterprise data warehouse
4. Types of enterprise data warehouse
5. Understanding the architecture of enterprise data warehouse
6. How VLink can help you deploy an enterprise data warehouse?
7. FAQs
What is an Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW)?
An enterprise data warehouse (EDW) is a company's central store for large data. In this sense, big data comprises anything from consumer data to company process-related data to personnel data. This information is often collected using several systems, including ERPs, CRMs, financial software, physical forms, and other data sources available to a company.
All data warehouse solutions have one thing in common: they ingest data, change it, transport it, and output it to the end user. The complexity of the design of business data warehouses, on the other hand, is substantially higher due to the sheer volume of data accessible.
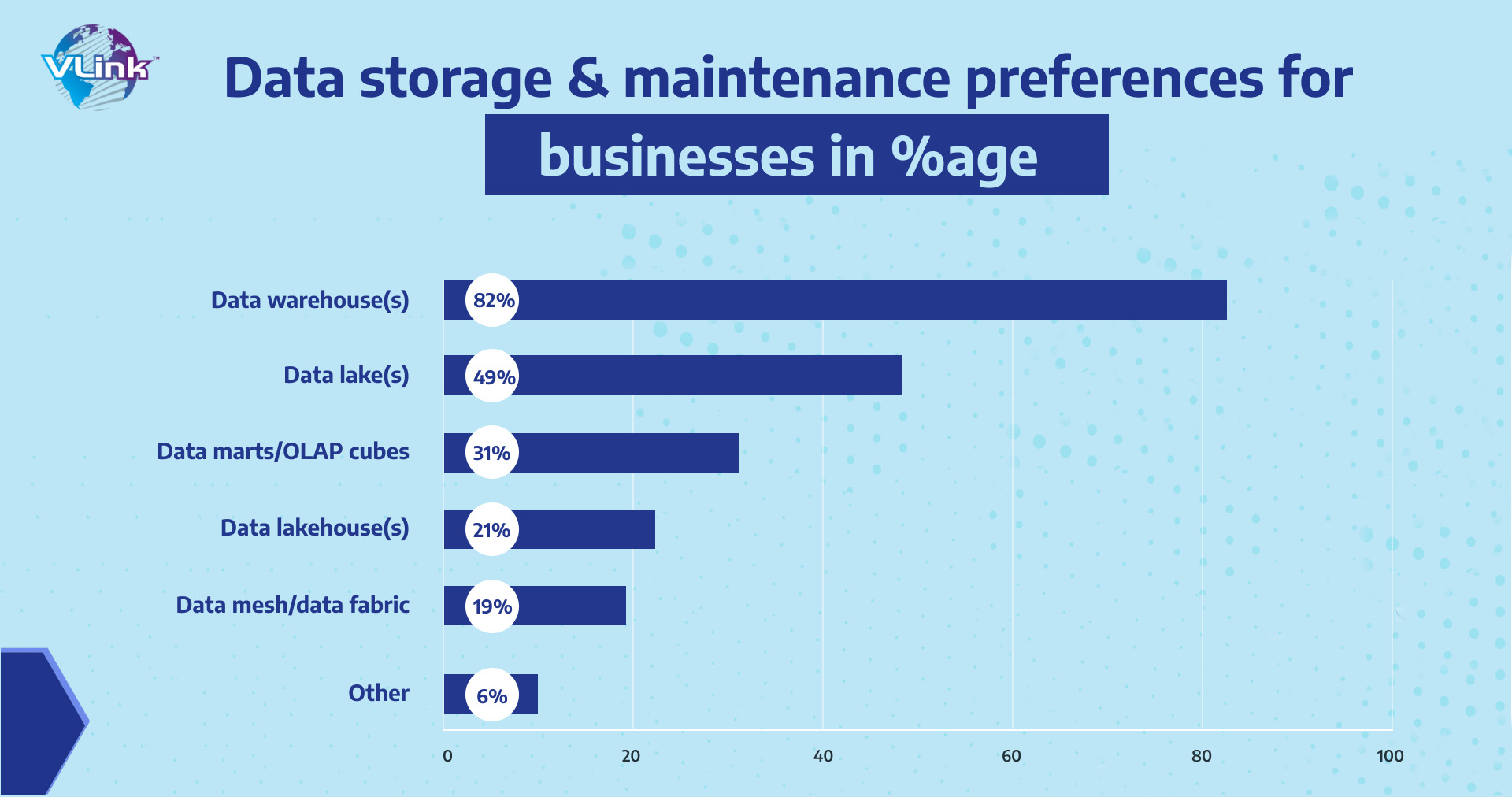
Because of this, most EDWs have distinct domain-specific datasets grafted on, allowing end-users to conduct queries pertaining to business units and functions.
Types of enterprise data warehouse
1- Classic Data Warehouse
A classic or on-premise data warehouse is a collection of hardware and software installed in a specific place to satisfy the needs of the business that acquired it. An on-premise data warehouse provides customers with increased speed, security, and management.
Who should make use of it: Classic EDWs are ideal for firms seeking a more personalized EDW. Depending on the demands of the business and industry, classic EDW can be transformed into a variety of architectural styles.
2- Virtual Data Warehouse
Virtual or cloud-based integrations with a data warehouse is a remotely situated data warehouse that is owned by a third party rather than the business entity that uses it. Only the services are paid for by the organization. A cloud-based platform is far less costly, more integrated, and scalable. However, there are significant drawbacks, such as network slowness and security.
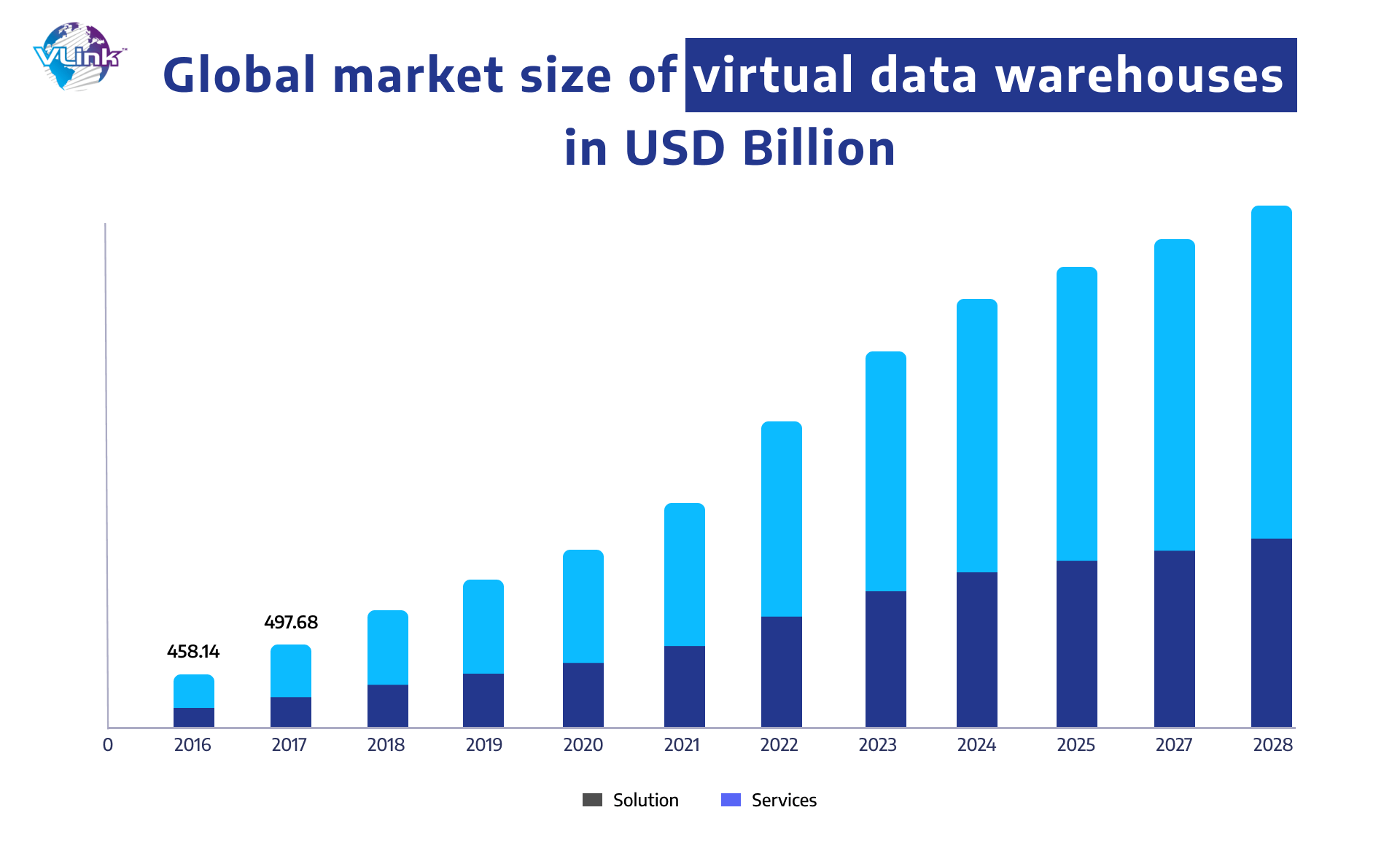
Who should make use of it: Virtual EDWs are appropriate for firms that deal with standardized raw data that does not necessitate complicated analyses. Businesses at the beginning of the analytics maturity curve, with little BI demands or skills, might profit from a virtual EDW.
3- Hybrid Data Warehouse
A hybrid data warehouse is one that combines on-premises and cloud data warehouses. It ensures compliance and allows for greater flexibility. This hybrid solution enables a corporation to benefit from both the efficiency of a traditional warehouse and the scalability of the cloud.
Who should use it: Cloud EDWs are the greatest alternative for all organizations and corporations. Cloud EDWs are ideal if you want a plug-and-play setup with managed data integration, EDW maintenance, and BI support.
Components of enterprise data warehouse
There are several tools available for establishing an enterprise data warehousing platform. Let's deep dive to understand each component's purpose and functions.
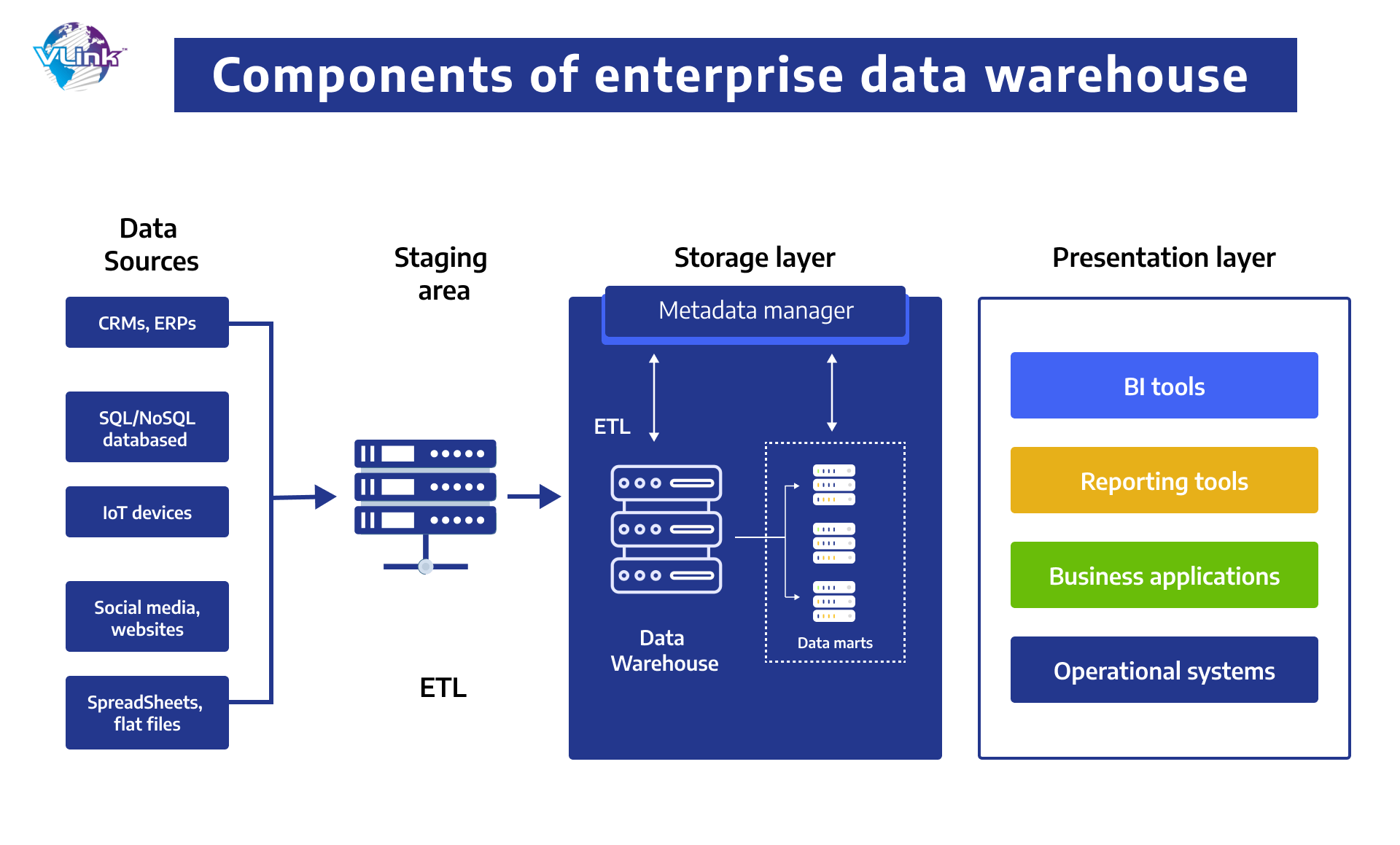
- Data sources
This component basically represents the location from where the data is picked, generated or saved. Data sources may be any file, spreadsheet, database, or a device.
- Staging phase
With the ELT technique, some modification may still be required here. However, at that point, all of the general modifications will be implemented, and the data will be imported into its final model(s). As previously stated, data warehouses are often relational databases. DW will also contain a database management system and extra metadata storage.
- Ingestion layer
Extract, transform, load (ETL) and extract, load, transform (ELT) are the two basic methods for extracting data from sources and delivering it to a warehouse. Before the data is loaded into an EDW, ETL transforms it in a staging area. ELT, a more recent technique, does all transformation activities within a warehouse. The staging area is missing in this case.
- Storage layer
Finally, the data is put into the storage space. Here, if you choose to deploy a modernized data warehouse, it will automatically segment the storage according to its type, usage, and format.
- Module for metadata
Simply said, metadata is information about information. These are the explanations that provide users/administrators with indications as to what subject/domain this information refers to. This data might be technical meta (for example, original source) or business meta (for example, sales area).
- Presentation layer
The final component of an EDW is tools that provide end users with data access. This layer, also known as the BI interface, will function as a dashboard for data visualization, business reporting, and extracting individual bits of information for activities such as machine learning.
Understanding the architecture of enterprise data warehouse
If we talk about a simple data warehouse, then it has three main components, namely a data layer (where data interchanges from data sources), a warehousing platform (where all the processes take place), and user-friendly interface or dashboard (included with business intelligence tools and data analytics).
Let's take a look at some of the most typical commercial approaches to corporate data warehouse design.
Single-tier architecture
A single-tier architecture is the most basic type of data warehouse design. A one-tier EDW normally means that your databases are directly connected to the analytical interfaces via which end users may query data. Here are some of its characteristics:
- Slower processing: This architecture can’t handle vast amounts of data for processing through BI tools and data analytics, as these processes can result in inaccurate query results and slower processing.
- Needs accurate inputs: Because you're querying data directly from the data warehouse, your queries must be quite specific in order to provide the correct results. This complicates data display.
- Restricted flexibility: You have restricted analytical capabilities and flexibility since your corporate data warehouse is directly coupled to the BI and analytics layer. You may be limited to doing extremely narrow searches and working with a small number of models. This results to less reporting complexity.
2-tier architecture
A data mart sits between the user interface and the EDW in a two-tier design. A data mart is a type of low-level database that exclusively stores domain-specific data. It stores data unique to business functions, making it easier for the EDW to conduct queries successfully.
Because business-domain-specific data is already structured at the data mart level, two-tier architecture provides higher output accuracy and quicker processing times.
3-tier architecture
On top of the data mart layer, three-tier EDWs have an online analytical processing (OLAP) cube, which is also one of the most prioritized data warehouse trends in the industry. An OLAP cube is a multidimensional data database.
Relational databases store information in two dimensions (similar to Excel or Google Sheets). In contrast, OLAP allows you to store data in numerous dimensions and facilitates mobility within these dimensions.
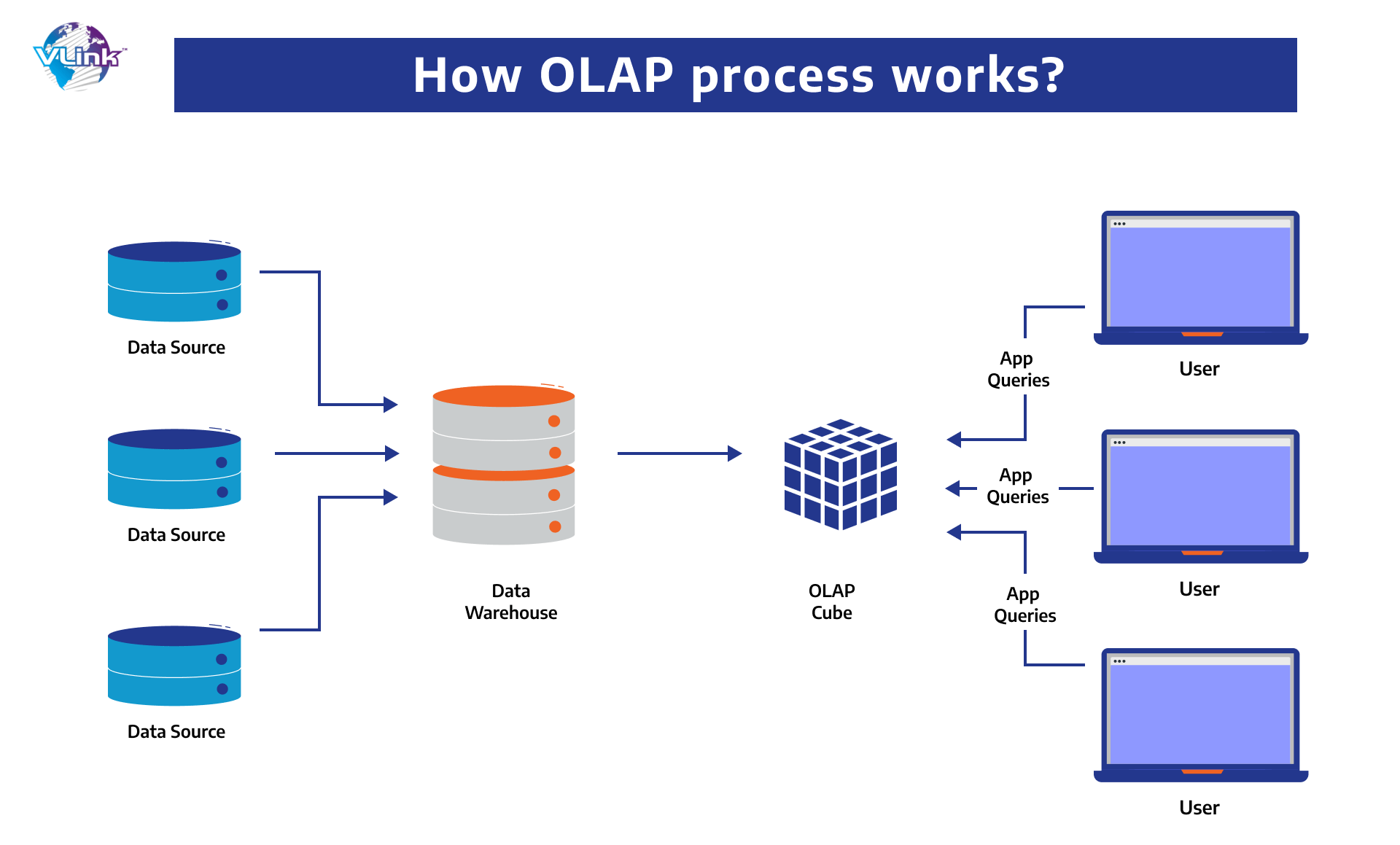
The most significant advantage of OLAP is that it allows end users to filter and slice data in order to produce comprehensive reports. You may go deeper into domain-specific data and execute more complex searches.
How VLink can help you deploy an enterprise data warehouse?
Building or installing a data warehouse is a time-consuming and resource-intensive endeavor, but the benefits outweigh the costs. With so many alternatives, selecting the finest data warehouse systems, ETL tools, and business intelligence tools for your needs may be difficult.
VLink has deployed enterprise data warehouse solutions for global clients and made sure they are performing according to their expectations. Our data experts know how to evaluate the business needs, scopes of optimizing traditional processing methods, and create data strategies to deploy the best platforms.
Just share your challenges and our data warehouse developers make sure to enhance your business efficiency and enable smart data-driven decision making.
FAQs
Frequently AskedQuestions
One of the most valuable assets of a corporation is the data contained in an EDW system. It comprises data that represents your complete business. Your departments may work in data silos if you do not have an EDW system.
A data warehouse is a consolidated data repository for reporting and analytics, sometimes known as a database of databases. An enterprise data warehouse (EDW) is a database or databases that holds data from many departments inside a company.
A comprehensive guide on constructing an enterprise data warehouse (EDW) requires step-by-step instructions, which includes:
- Define the needs of the company.
- Examine the source data.
- Create data models that are conceptual, logical, and physical.
- Determine and create a data warehouse schema.
- Implement a data warehouse architecture in stages.
Other factors that will depend on this process are - what type of enterprise data warehouse your business needs, budget of your company, and availability of existing storage.