Since customers have different expectations from insurance companies than they did a decade ago, the adoption of the latest technologies has become critical.
People desire simplicity in all aspects of their lives. They prefer digital connections to in-person meetings and want to manage their policies without leaving their homes. At the same time, buyers value customization more than ever. They demand personalized care whenever they need it, in addition to self-service options.
And you can simply anticipate these expectations by implementing top insurtech trends mentioned in this blog.
We’ve have listed all the future trends of the insurance industry to help your business.
8 Future trends in the insurance industry
1- Low code/no-code development in insurtech trends
Historically, digital transformation depended on costly IT personnel to deploy and maintain numerous digital channels. However, with the rise of low-code and no-code platforms, insurers may now deploy digital apps with little or no computer programming.
Low-code/no-code software can minimize the time it takes to deploy insurance technology applications from months to a few hours.
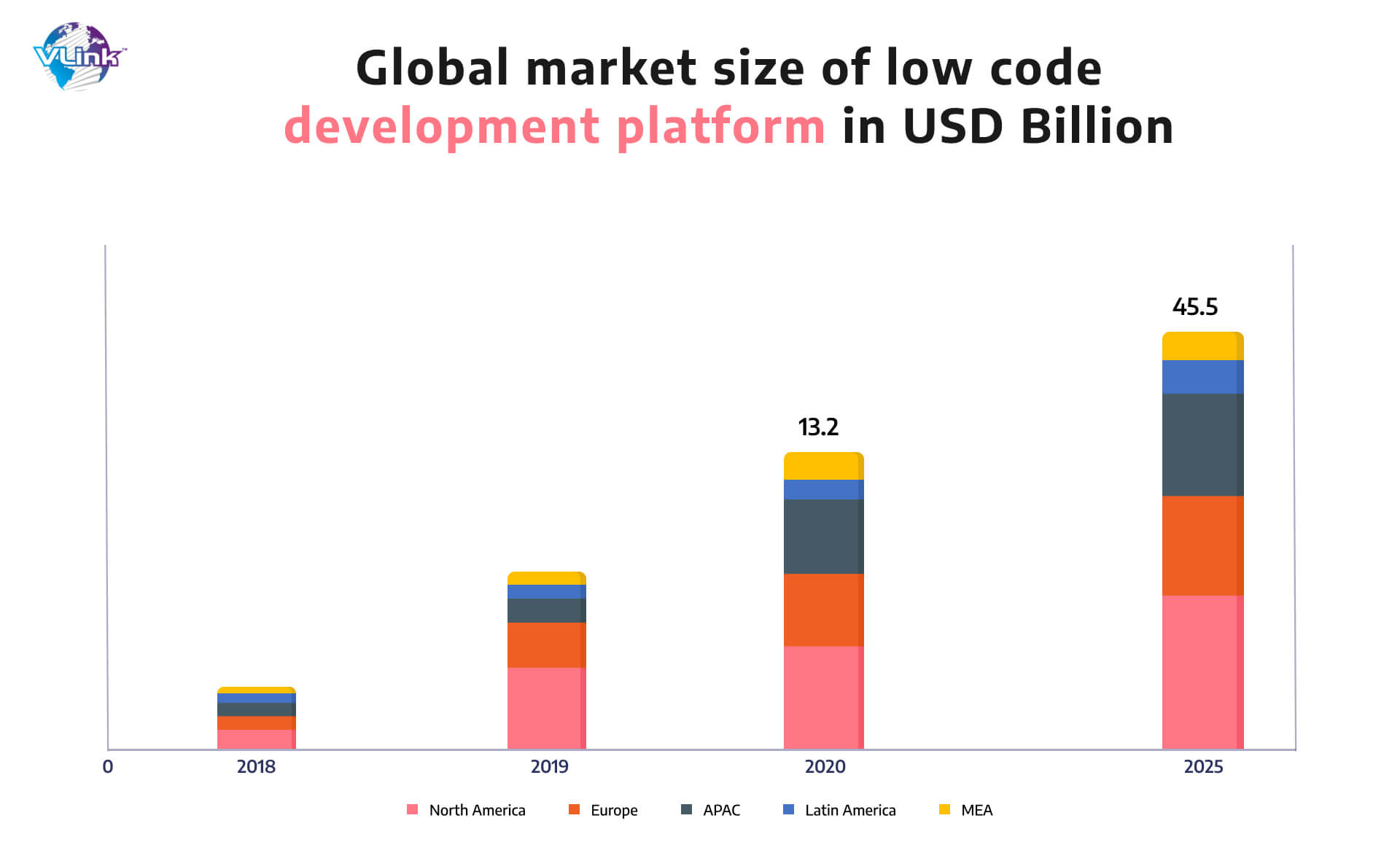
They are not, however, intended to replace IT departments. Rather, they allow IT to more strategically employ their technological resources. Low-code/no-code development solutions are recommended to integrate with the best practices of software development lifecycle in collaboration with IT.
2- Customer experience design for insurtech apps
Customers have always been the center of focus for insurance businesses, but the emergence of digital technology has made their approach optimized in terms of seeking quality experience.
Previously, customer surveys and other types of market research were the key assets for insurers to grab their potential audience’s data. But now, they have a broader range of sources, such as social media, online browser statistics, and even wearable devices. The integration of data analytics and smart information processing is helping insurance companies to break down silos in improving the customer experience.
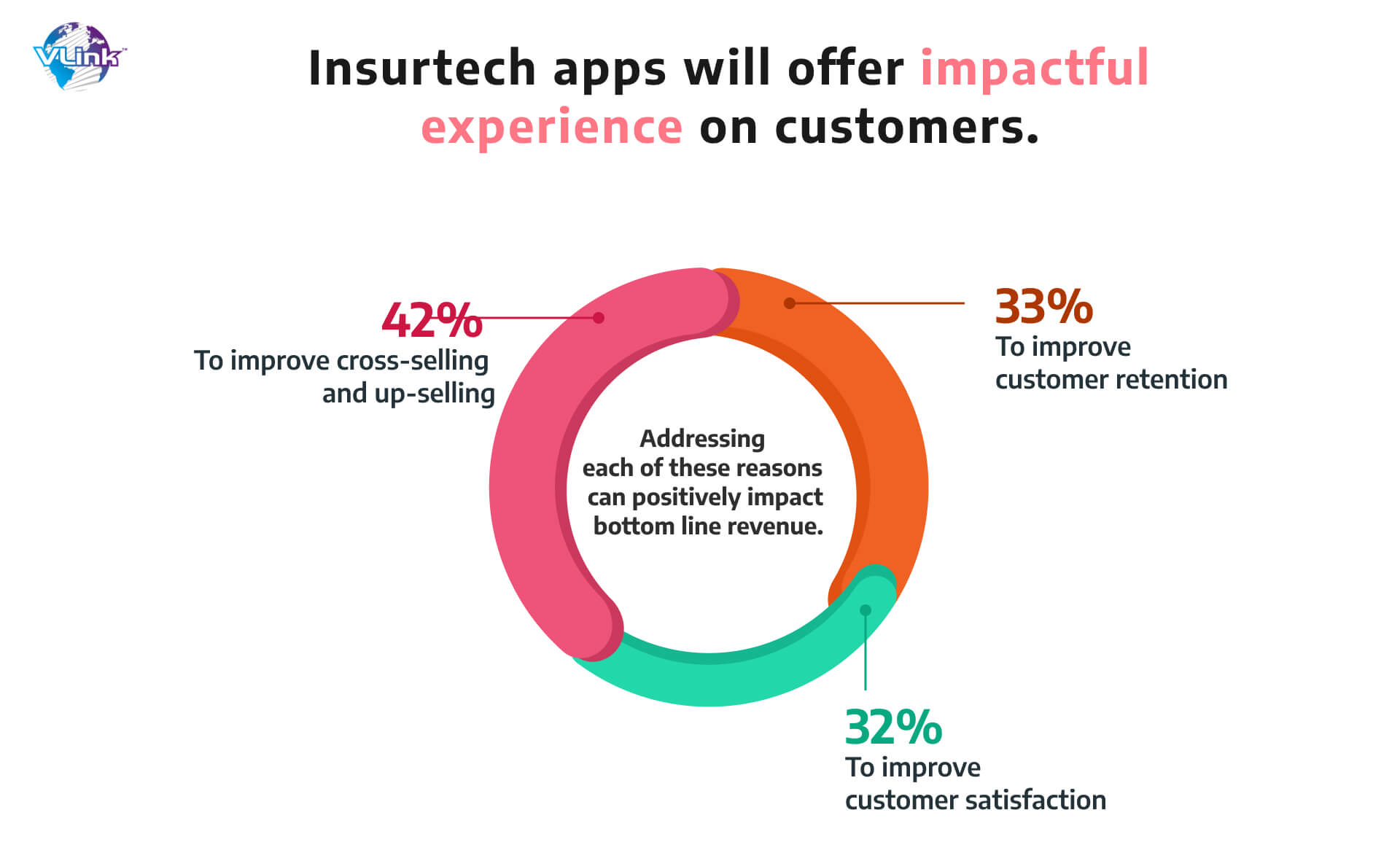 Moreover, insurers are boosting their investments in digital self-service technologies such as automated feedback/response generators and chatbots. Customers can use these tools to access the information they need without having to wait on hold or negotiate difficult processes.
Moreover, insurers are boosting their investments in digital self-service technologies such as automated feedback/response generators and chatbots. Customers can use these tools to access the information they need without having to wait on hold or negotiate difficult processes.
3- Open APIs for Insurtech app trends
Open APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are application programming interfaces, publicly available to allow developers to access a software application or online service. They also control how apps communicate and interact with one another.
A private API, as opposed to an open API, is maintained by its own in-house developers. And therefore, they are mostly utilized for back-end data processing and application tasks. They enable insurance businesses to exhibit their services to the outside world, allowing other partners to utilize them and give value to their clients.
According to Accenture, 82% of insurers support the adoption of open IT ecosystems that allow their businesses to grow while 59% of them are planning to integrate them with their new business models.
Enterprises linked by APIs can form an insurance technology ecosystem to give a best-of-breed consumer experience by combining digital services from several enterprises.
Also Read: How to Find & Hire Fintech App Developers
4- Hybrid cloud architecture for insurance app security
Organizations are increasingly using hybrid clouds in order to capitalize on the benefits of both cloud and public clouds. Hybrid cloud architectures boost both speed and flexibility by allowing organizations to switch between their own tools and the toolkits of cloud providers.
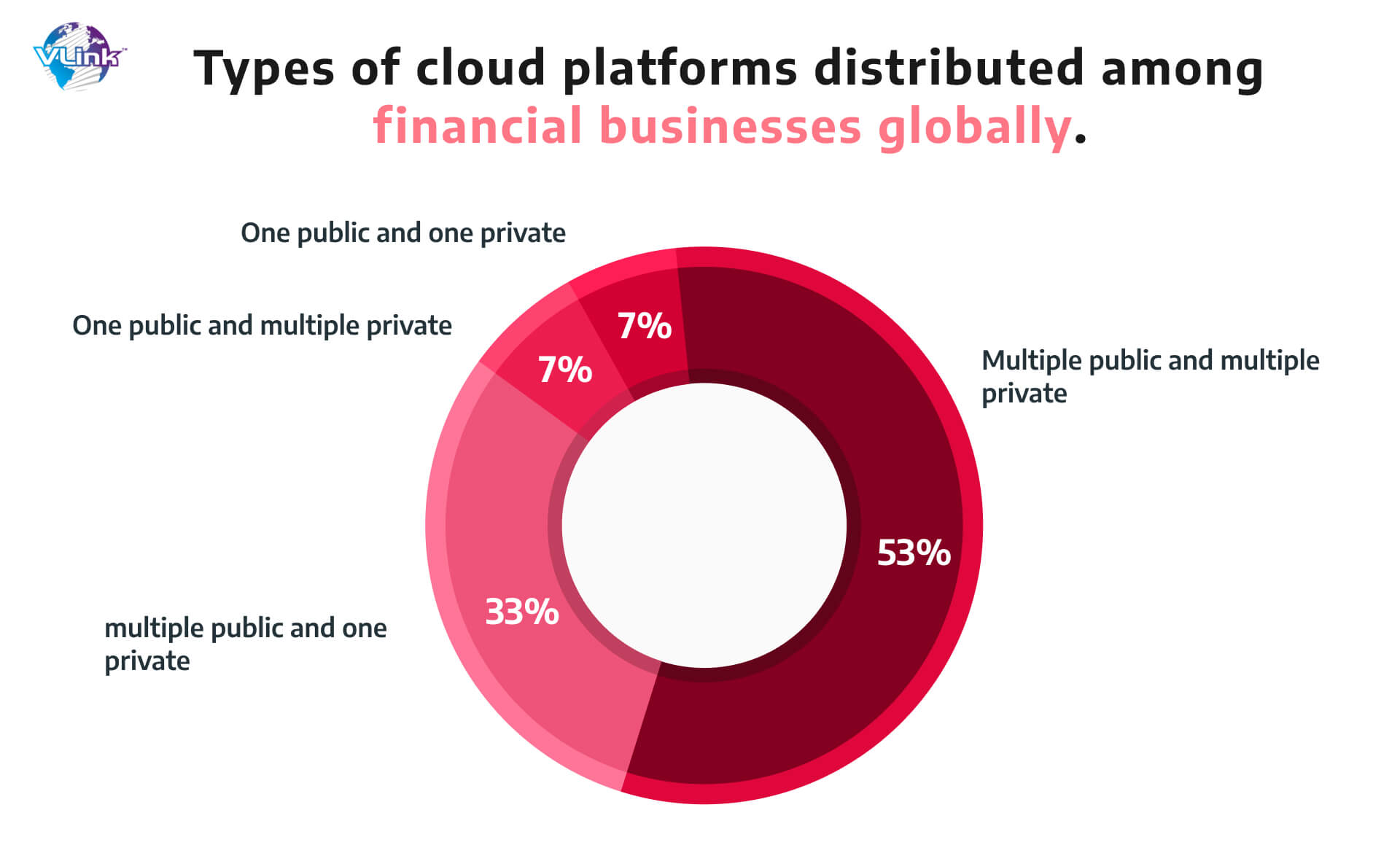 With this background, current insurance market developments would represent a refinement of this method. Core business processes will be migrated to the cloud and tightly integrated with various insurance technology tools and platforms to create a digitally native insurance ecosystem.
With this background, current insurance market developments would represent a refinement of this method. Core business processes will be migrated to the cloud and tightly integrated with various insurance technology tools and platforms to create a digitally native insurance ecosystem.
Telematics is a technology that allows for the tracking of data around a vehicle's movements, and insurers are increasingly using it to acquire information about their clients' driving patterns.
The need to provide more personalized pricing to clients is driving the development of telematics-based insurance solutions. Insurers can better analyze the risk involved and price their insurance if they know how and when their customers drive.
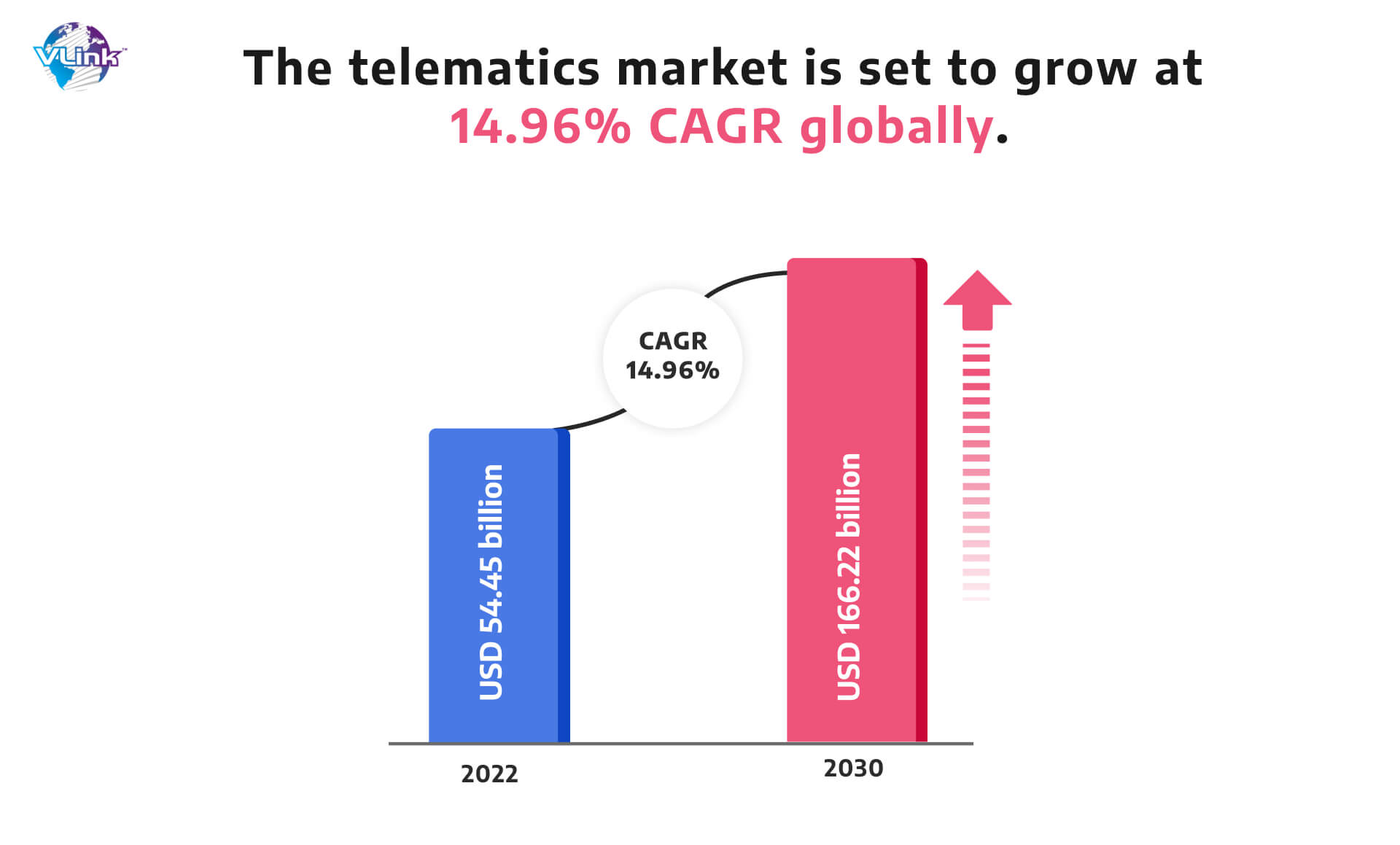 Furthermore, telematics may be utilized to detect fraudulent behavior. For example, if an insured motorist is seen to be driving in a reckless manner that is likely to result in an accident, their insurance coverage may be cancelled.
Furthermore, telematics may be utilized to detect fraudulent behavior. For example, if an insured motorist is seen to be driving in a reckless manner that is likely to result in an accident, their insurance coverage may be cancelled.
Customers used to take in-person assessments in conventional insurance underwriting. However, following the COVID-19 epidemic, this was no longer an option, and many insurers were forced to embrace expedited underwriting, aided by digital self-service tools and insurance technology.
The availability of big data, expanding demographic statistics, and limited face-to-face encounters have aided the proliferation of expedited underwriting programs in the life insurance sector. According to LIMRA’s survey, 53% of consumers prefer simplified underwriting from insurance agencies while buying a life insurance.
Furthermore, predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms in underwriting programs make it simpler and faster for clients to receive life insurance coverage by bypassing traditional time-consuming underwriting processes.
The data analytics environment has changed dramatically in recent years. Agents may now select from a wide range of tools and approaches to undertake reliable predictive analysis. They must abandon manual processes if they want to remain competitive and meet the criteria established by Insurtech experts.
The technology works so well that 60% of insurers experienced a rapid boost in sales while seeing a 67% decrease in overall expenses.
Predictive analytics works by putting historical data into models that are developed over time (machine learning), resulting in predictions about trends and behavior patterns. This allows insurance businesses to make better educated judgements regarding quoting, workload optimization, product recommendations, and other topics.
Life and health insurance businesses are increasingly using artificial intelligence and other predictive analytics to generate better preventative risk measures for their consumers.
The AI-powered technologies help insurance operations and claims resolution teams. However, the utility of Machine Learning extends beyond claims processing; it has the potential to assist insurers in automating the entire process. As data become more digitized, they may be quickly analyzed using AI algorithms, removing the need for manual processing completely.







